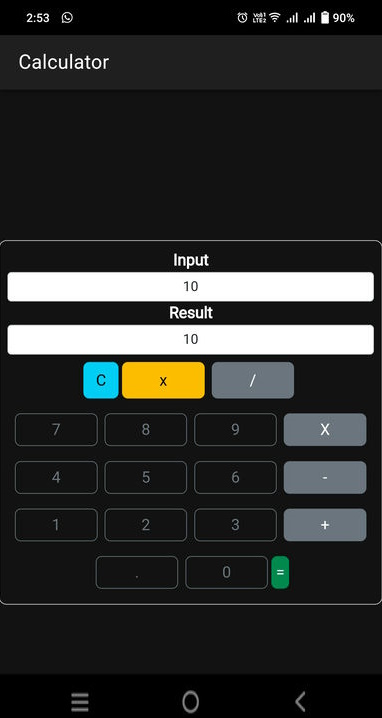
We will discover how to use the Ionic framework to construct a mobile application in this tutorial. With the help of the open-source Ionic user interface tool, which integrates with well-known frameworks like Angular, React, and Vue, we can create professional mobile applications with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.

Both iOS and Android are supported.
Pre-requisite
To start with Ionic Framework, the only requirement is a Node & npm environment, Andriod Studio, command line interface, and Visual Studio code as a code editor.
Step 1. Install ionic
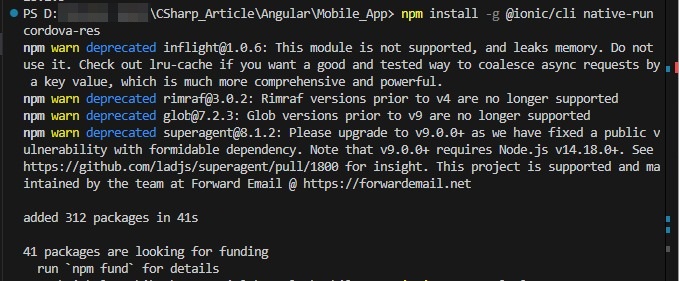
The first step is we need to install ionic tooling. Run the below command to install ionic CLI.
- native-run: Used to run native binaries on devices and simulators/emulators.
- cordova-res: Used to generate icons and splash screens for the native app.
npm install -g @ionic/cli native-run cordova-res
Step 2. Create an Application
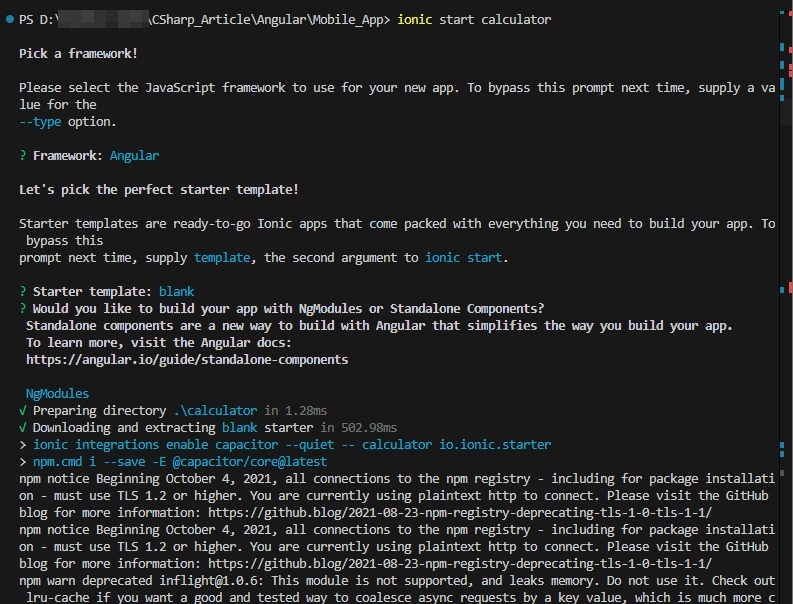
Run the below command to create an ionic application. We will create a calculator for this article’s explanation. Check out the below screen prints for command execution.
ionic start calculator
Step 3. Write an Application Code
home.page.html
<ion-header [translucent]="true">
<ion-toolbar>
<ion-title>
Calculator
</ion-title>
</ion-toolbar>
</ion-header>
<ion-content [fullscreen]="true">
<ion-header collapse="condense">
<ion-toolbar>
<ion-title size="large">Blank</ion-title>
</ion-toolbar>
</ion-header>
<div id="container">
<div class="jumbotron col-sm-4 p-2 m-0 bg-inverse mx-auto" style="border: 1px solid lightgray; border-radius: 2%;">
<label style="font-weight: bolder;">Input</label>
<div class="input-group input-group-sm col-sm-12 m-0 p-0">
<div class="col-sm-12 form-control text-lg-right" type="text">{{input}}</div>
</div>
<label style="font-weight: bolder;">Result</label>
<div class="input-group input-group-sm col-sm-12 m-0 p-0">
<div class="form-control text-sm-right" type="text">{{result}}</div>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-12 p-1 m-0">
<button class="btn btn-info col-sm-6" type="button" (click)="allClear()">C</button>
<button class="btn btn-warning col-sm-3" type="button" (click)="clear()">x</button>
<button class="btn btn-secondary col-sm-3" type="button" (click)="pressOperator('/')">/</button>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-12 p-1 m-0">
<button class="btn btn-outline-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="clickNum('7')">7</button>
<button class="btn btn-outline-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="clickNum('8')">8</button>
<button class="btn btn-outline-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="clickNum('9')">9</button>
<button class="btn btn-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="pressOperator('*')">X</button>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-12 p-1 m-0">
<button class="btn btn-outline-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="clickNum('4')">4</button>
<button class="btn btn-outline-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="clickNum('5')">5</button>
<button class="btn btn-outline-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="clickNum('6')">6</button>
<button class="btn btn-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="pressOperator('-')">-</button>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-12 p-1 m-0">
<button class="btn btn-outline-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="clickNum('1')">1</button>
<button class="btn btn-outline-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="clickNum('2')">2</button>
<button class="btn btn-outline-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="clickNum('3')">3</button>
<button class="btn btn-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="pressOperator('+')">+</button>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-12 p-1 m-0">
<button class="btn btn-outline-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="clickNum('.')">.</button>
<button class="btn btn-outline-secondary col-sm-3 p-1" type="button" (click)="clickNum('0')">0</button>
<button class="btn btn-success col-sm-6 p-1" type="button" (click)="getAnswer()">=</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</ion-content>
home.page.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-home',
templateUrl: 'home.page.html',
styleUrls: ['home.page.scss'],
})
export class HomePage {
input: string = '';
result: string = '';
clickNum(num: string) {
// Do Not Allow . more than once
if (num == ".") {
if (this.input != "") {
const lastNum = this.getLastOperand();
console.log(lastNum.lastIndexOf("."));
if (lastNum.lastIndexOf(".") >= 0) return;
}
}
// Do Not Allow 0 at beginning.
// Javascript will throw Octal literals are not allowed in strict mode.
if (num == "0") {
if (this.input == "") {
return;
}
const PrevKey = this.input[this.input.length - 1];
if (PrevKey === '/' || PrevKey === '*' || PrevKey === '-' || PrevKey === '+') {
return;
}
}
this.input = this.input + num;
this.calcAnswer();
}
getLastOperand() {
let pos: number;
console.log(this.input);
pos = this.input.toString().lastIndexOf("+");
if (this.input.toString().lastIndexOf("-") > pos) pos = this.input.lastIndexOf("-");
if (this.input.toString().lastIndexOf("*") > pos) pos = this.input.lastIndexOf("*");
if (this.input.toString().lastIndexOf("/") > pos) pos = this.input.lastIndexOf("/");
console.log('Last ' + this.input.substr(pos + 1));
return this.input.substr(pos + 1);
}
pressOperator(op: string) {
// Do not allow operators more than once
const lastKey = this.input[this.input.length - 1];
if (lastKey === '/' || lastKey === '*' || lastKey === '-' || lastKey === '+') {
return;
}
this.input = this.input + op;
this.calcAnswer();
}
clear() {
if (this.input != "") {
this.input = this.input.substr(0, this.input.length - 1);
}
}
allClear() {
this.result = '';
this.input = '';
}
calcAnswer() {
let formula = this.input;
let lastKey = formula[formula.length - 1];
if (lastKey === '.') {
formula = formula.substr(0, formula.length - 1);
}
lastKey = formula[formula.length - 1];
if (lastKey === '/' || lastKey === '*' || lastKey === '-' || lastKey === '+' || lastKey === '.') {
formula = formula.substr(0, formula.length - 1);
}
console.log("Formula " + formula);
this.result = eval(formula);
}
getAnswer() {
this.calcAnswer();
this.input = this.result;
if (this.input == "0") this.input = "";
}
}
home.page.scss
#container {
text-align: center;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
right: 0;
top: 50%;
transform: translateY(-50%);
}
#container strong {
font-size: 20px;
line-height: 26px;
}
#container p {
font-size: 16px;
line-height: 22px;
color: #8c8c8c;
margin: 0;
}
#container a {
text-decoration: none;
}
.col-sm-3 {
flex: 0 0 auto;
width: 23%;
margin: 1%;
}
@media (min-width: 576px) {
.col-sm-3 {
flex: 0 0 auto;
width: 23%;
margin: 1%;
}
}
.form-control{
min-height: 30px;
}
Step 4. Add required packages
We can add third-party packages as per requirements. Here for this demo, I have used Bootstrap to make the UI smooth. Run the below command to install the Bootstrap.
Move to the application path using the below command.
cd calculator
npm i bootstrap bootstrap-icons
ng add @ng-bootstrap/ng-bootstrap
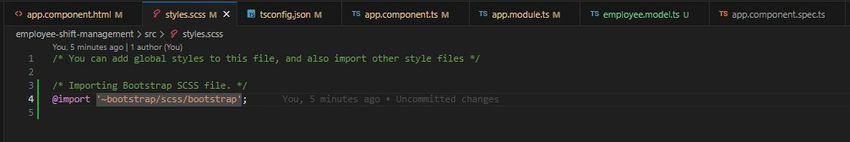
Import bootstrap to styles.scss file located at the root level.
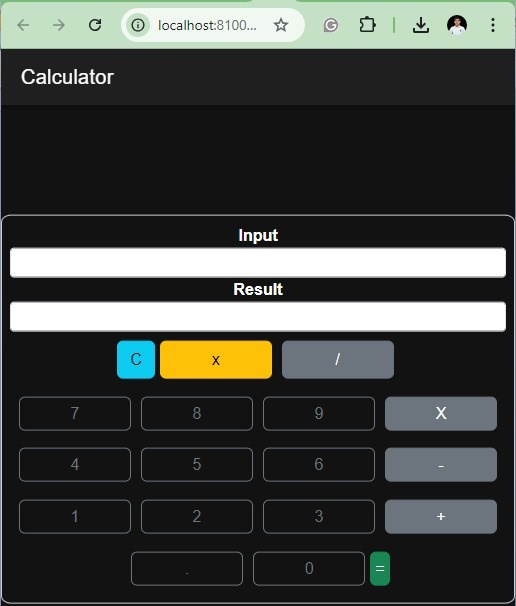
Step 5. Run the Application with Browser
Run the below command to execute the application in a browser.
ionic serve
You can examine the folder structure and the created/generated www folder as soon as the application launches in the browser. All of the JavaScript code generated for the application is stored in the www folder. This is a www, similar to the dist folder in an Angular application. For an example, view the screen print below.
Step 6. Install the Android SDK
Once all application runs on the browser, we now need to run the same application on mobile devices like iOS or Android. For this article demonstration, I’m using an Android device. So I’ll generate the .apk file.
Now, let’s see how we can generate the APK file.
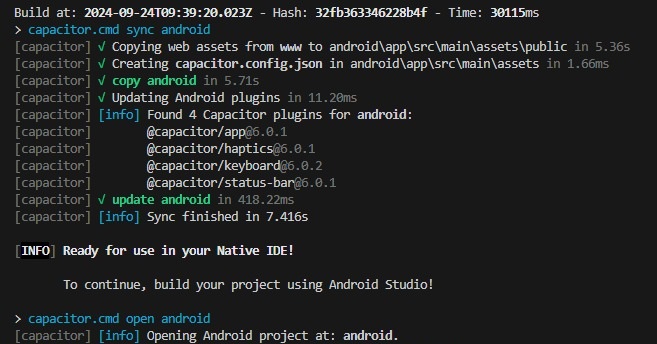
Let’s first run the below command in the terminal of the application path to generate apk.
ionic capacitor build android
If Android Studio is installed it will show a response like the below screen print, otherwise, you need to install Android Studio.
On My machine, I have already Android Studio installed. But you can get Android Studio from the mentioned path and get installed like the below screen print
Android Studio SDK path. Sometimes it takes time to download all required packages and it throws errors like the below screen print.
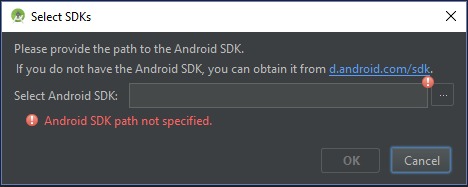
You can just close the error popup and close the project. It will start downloading pending packages and once all required packages are installed it will show a screen like below with the SDK path.
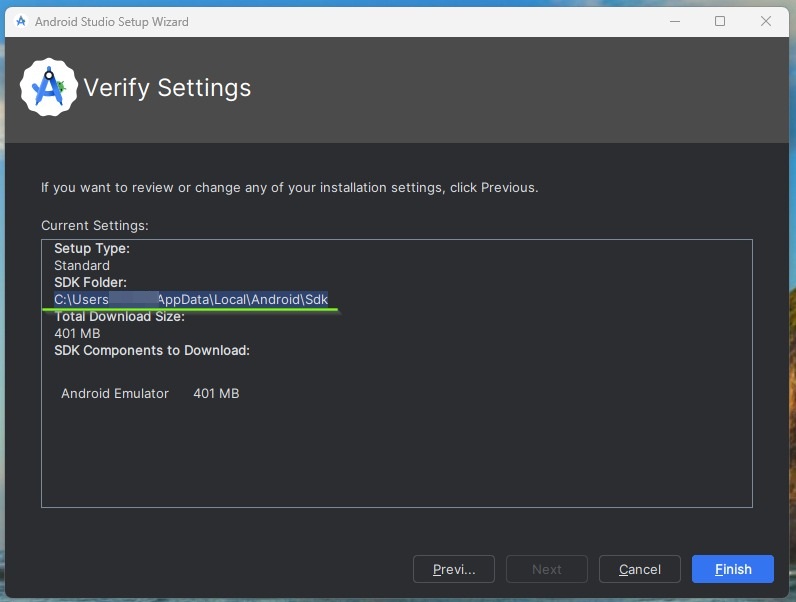
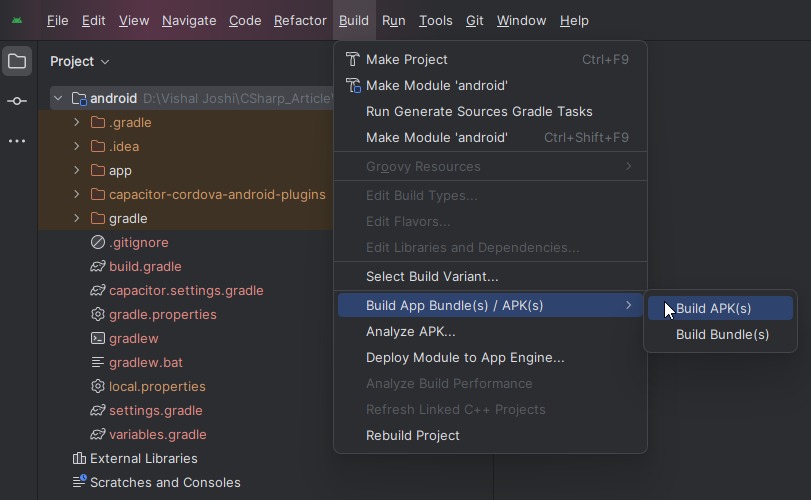
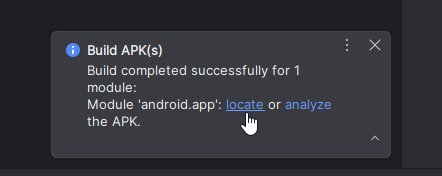
Step 7. Build the APK
Once the Android studio setup is done we can build apk file. To build apk file go to android studio -> build -> Build App Bundle(s) / APK(s) -> Build APK(s)
While building apk it will show the status like the below screen print.
Once APK generated you can click on locate and see the apk file.
Let’s install the APK file on an Android device.
Installed calculator application then let’s run application on the Android mobile device.