For Angular Caching issue, a service worker is a script that runs in the web browser and manages caching for an application. Service workers augment the traditional web deployment model and empower applications to deliver a user experience with reliability and performance on par with code that is written to run on your operating system and hardware. Adding a service worker to an Angular application is one of the steps for turning an application into a Progressive Web App (also known as a PWA).

At its simplest, a service worker is a script that runs in the web browser and manages caching for an application.
Service workers function as a network proxy. They intercept all outgoing HTTP requests made by the application and can choose how to respond to them. For example, they can query a local cache and deliver a cached response if one is available. Proxying isn't limited to requests made through programmatic APIs, such as fetch; it also includes resources referenced in HTML and even the initial request to index.html. Service worker-based caching is thus completely programmable and doesn't rely on server-specified caching headers.
Unlike the other scripts that make up an application, such as the Angular application bundle, the service worker is preserved after the user closes the tab. The next time that browser loads the application, the service worker loads first, and can intercept every request for resources to load the application. If the service worker is designed to do so, it can completely satisfy the loading of the application, without the need for the network.
Even across a fast reliable network, round-trip delays can introduce significant latency when loading the application. Using a service worker to reduce dependency on the network can significantly improve the user experience.
Note:
Below, until Run the App with Service Worker, the procedure we follow are mainly from
Simulating a network issue
To simulate a network issue, disable network interaction for your application.
In Chrome:
Select Tools > Developer Tools (from the Chrome menu located in the top right corner).
Go to the Network tab.
Select Offline in the Throttling dropdown menu.
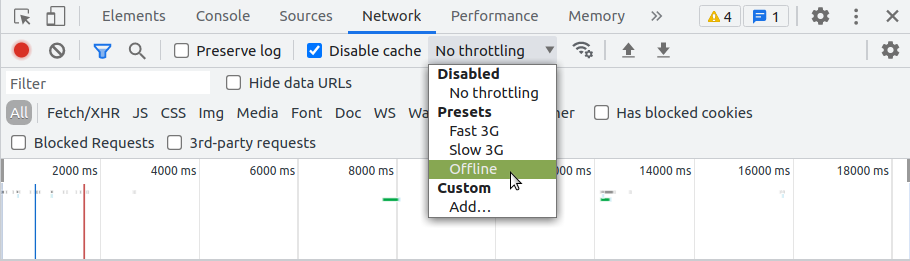
Now the application has no access to network interaction.
For applications that do not use the Angular service worker, refreshing now would display Chrome's Internet disconnected page that says "There is no Internet connection".
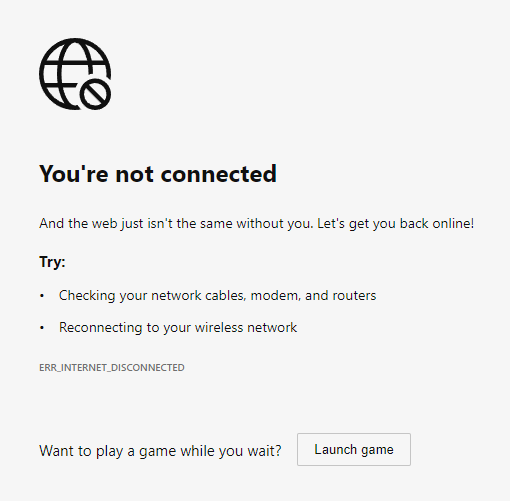
Install Service Worker
We install the Service Worker by the command:
ng add @angular/pwa
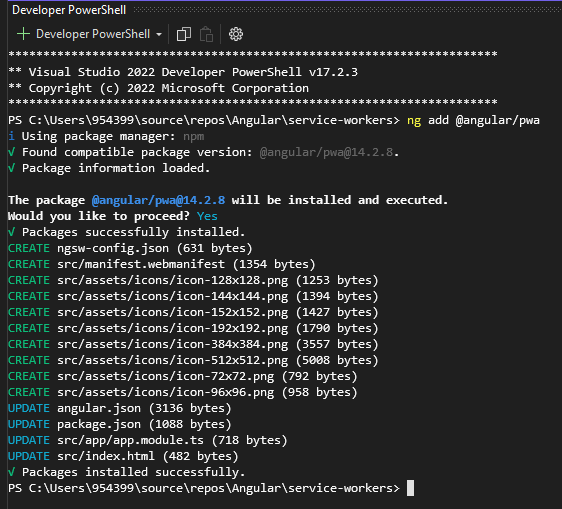
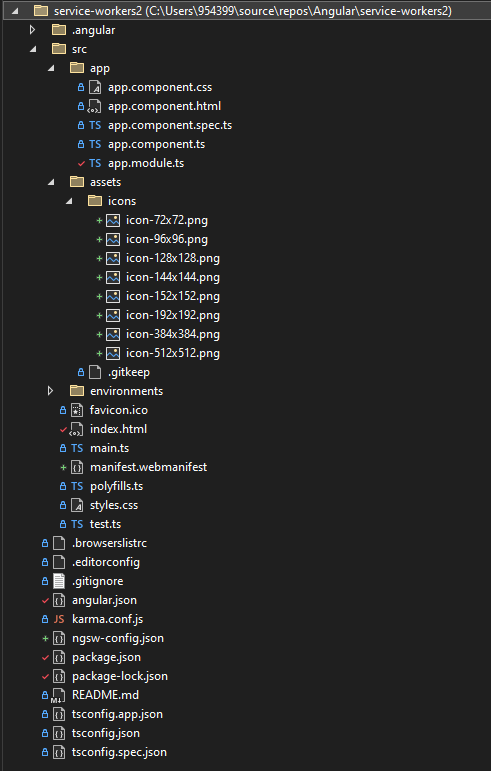
The files are installed or changed are
Changed:
app.module.ts
index.html
angular.json
package.json
package-lock.json
New Created:
manifest.webmanifest
ngsw-config.json
assets\icons folder
The preceding command completes the following actions:
Update app.module.ts file:
Adds the @angular/service-worker package to your project.
Enables service worker build support in the CLI.
Imports and registers the service worker in the application module.
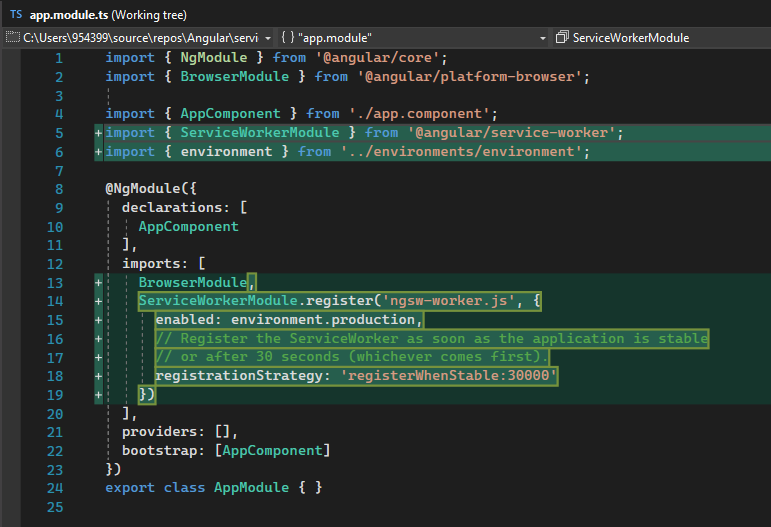
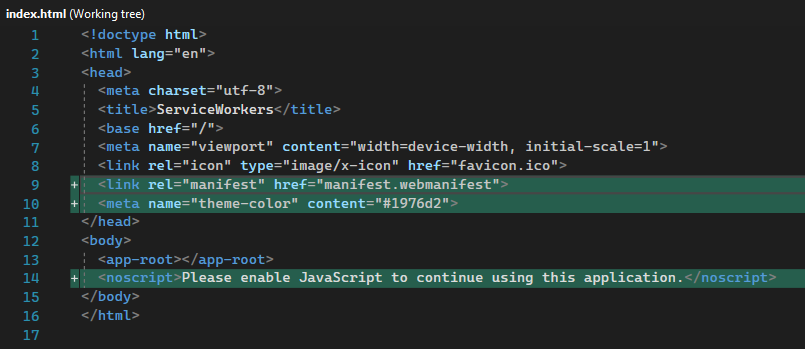
Updates the index.html file:
Includes a link to add the manifest.webmanifest file
Adds a meta tag for theme-color
Installs icon files to support the installed Progressive Web App (PWA).
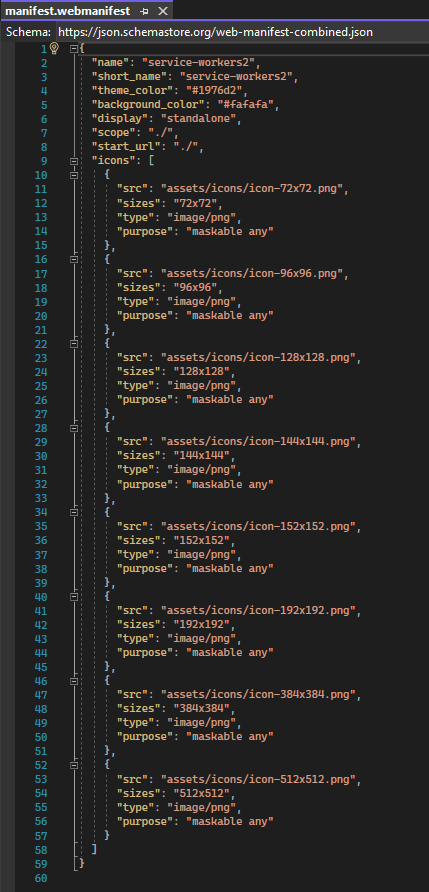
Creates installed icons registered file, called: manifest.webmanifest
Creates the service worker configuration file called ngsw-config.json, which specifies the caching behaviors and other settings.
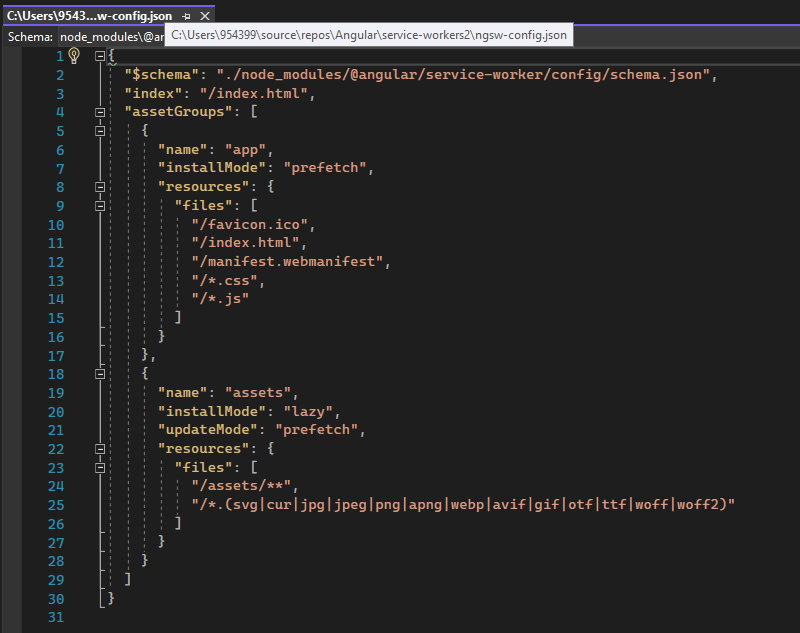
Updates the angular.json file, under "build"
Register file: manifest.webmanifest
Register file: ngsw-config.json
Register Servuce Worker as true
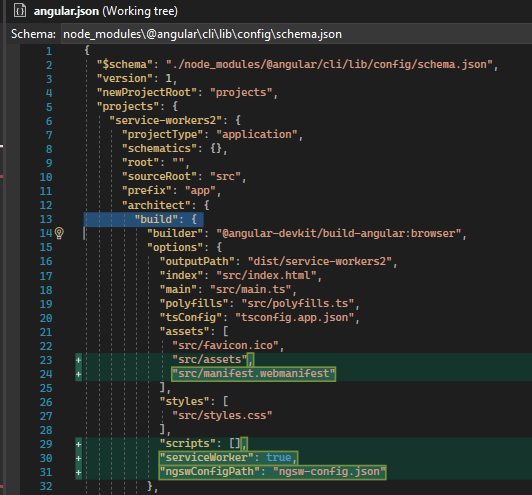
Updates the j.json file: the @angular/service-worker, 14.2.0 is added in dependencies
Install HTTP Server
Globally Installation via npm:
npm install --global http-server
Run the App with Service Worker
Note:
As we noticed the Service Worker installed is only registered to Build environment, not for Dev environment. So, to use Service Worker, we have to build the app.
ng build
Open the server at post 8080 for the project service-workers2:
by command: http-server -p 8080 -c-1 dist/<project-name>
Run the app at port 8080 with Service Worker:
Select Offline in the Throttling dropdown menu.
With the addition of an Angular service worker, the application behavior changes. On a refresh, the page loads normally. Look at the Network tab to verify that the service worker is active.
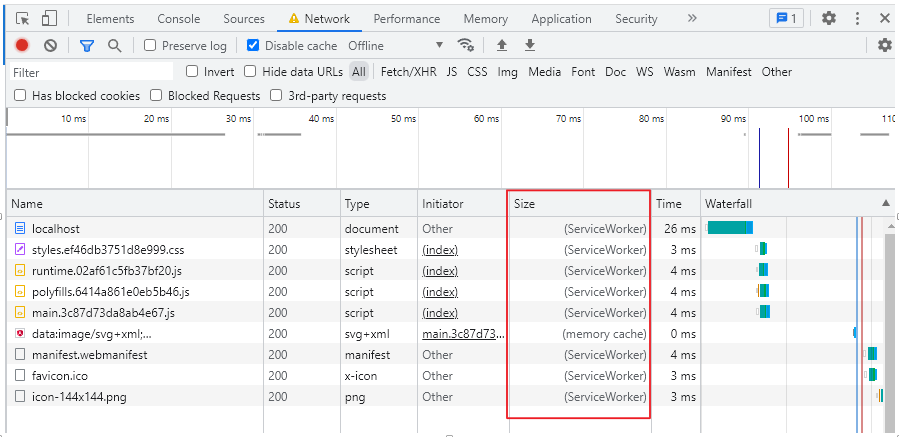
NOTE:
Under the "Size" column, the requests state is (ServiceWorker). This means that the resources are not being loaded from the network. Instead, they are being loaded from the service worker's cache.
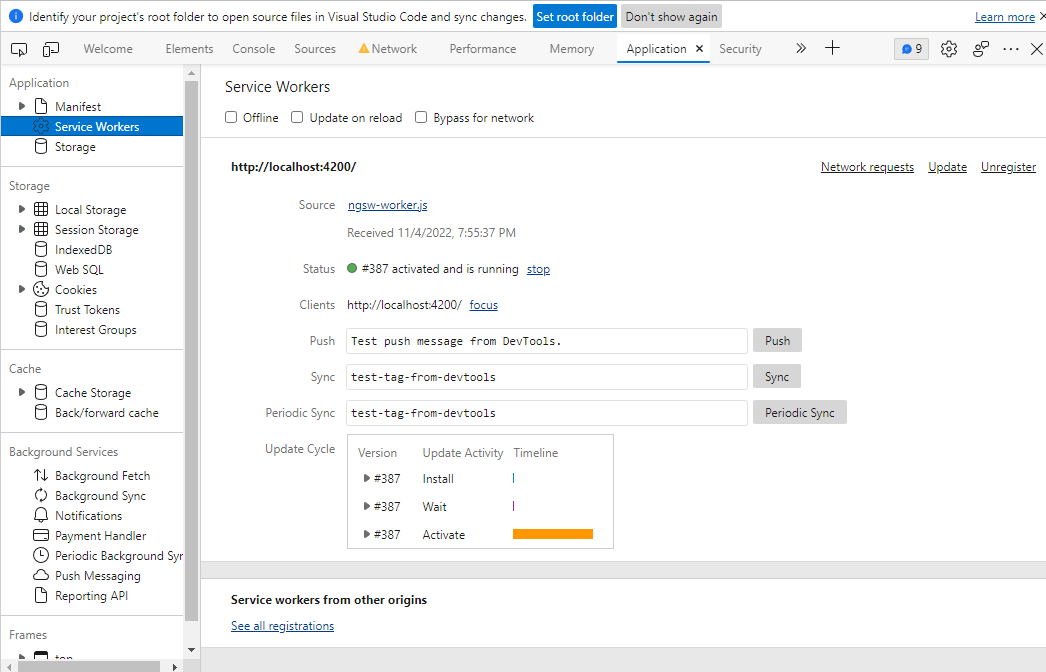
G - Verify if a service worker is registered #
To verify if a service worker is registered, use developer tools in your favorite browser.
In Firefox and Chromium-based browsers (Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, or Samsung Internet):
Open developer tools, then click the Application tab.
In the left pane, select Service Workers.
Check that the service worker's script URL appears with the status "Activated". (You'll learn what this status means in the lifecycle section in this chapter). On Firefox the status can be "Running" or "Stopped".
H - Summary
We demonstrated how to install Service Worker for solving Angular Caching issue.